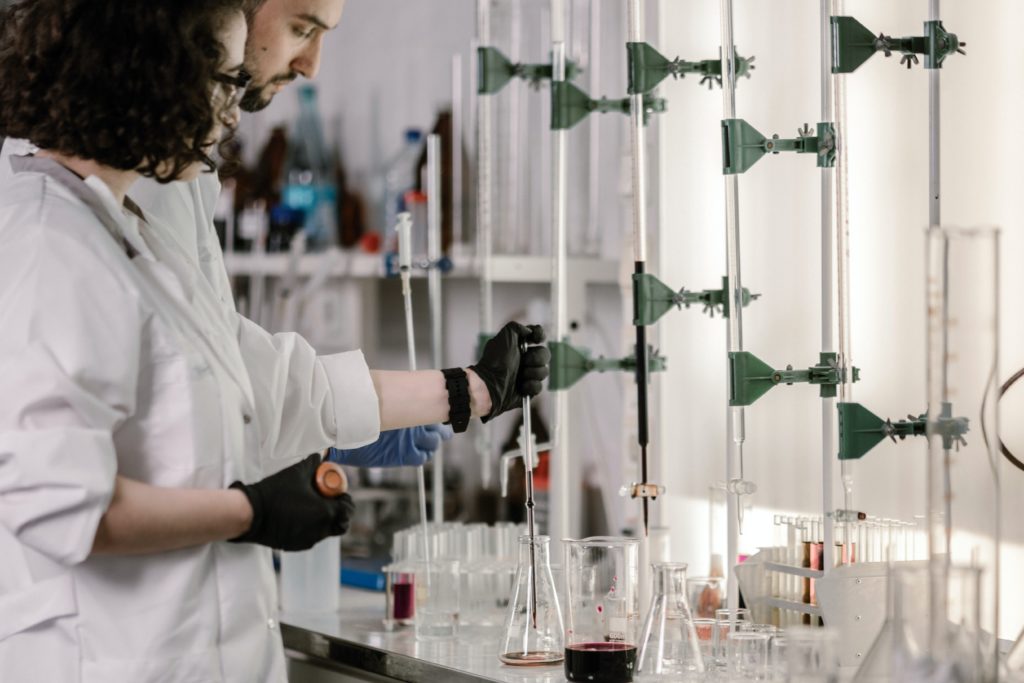
This can be done by using enzymes, plants and microorganisms to produce energy, industrial chemicals and consumer goods. Essentially industrial biotechnology is using biomolecules which are substances produced by cells and living organisms. Industrial biotechnology is important because it could generate bioproducts, biofuels and biopolymers that reduce environmental impact.
An example of industrial biotechnology is biomass which uses plant material like wood or food waste to produce heat or electricity.
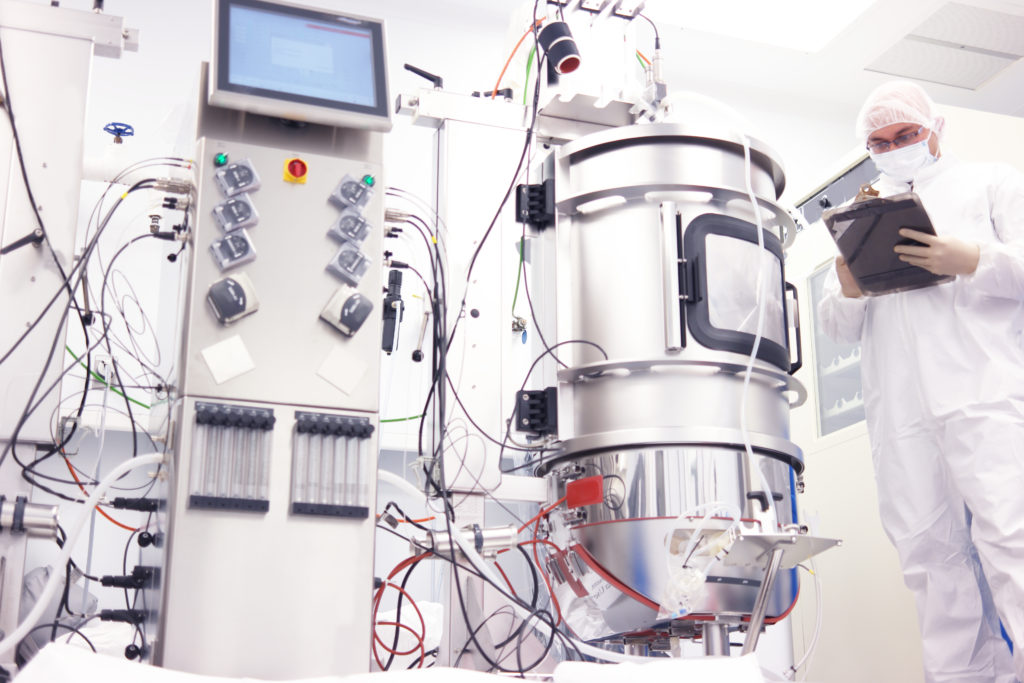

An example of industrial biotechnology is biomass which uses plant material like wood or food waste to produce heat or electricity.


























Site by Habit